Data, Computing, and Blockchain: The Fate of the Metaverse (Part 1)
The word “Metaverse” can be traced back to Neal Stephenson’s 1992 science fiction Snow Crash. Now three decades later, this word refers to a virtual world enabled by information technologies that is parallel to and co-existent with the physical world. It is a digital space where people live and interact under new social rules, and the migration from the physical world to the digital world is a process to be accompanied by large amounts of content creation, economic infrastructure building, user experience optimization and physical world mirroring.
The popularization of the Internet has made people’s lives increasingly digital. We depend on our smartphones for shopping, entertainment, traveling and ordering food. As we do these things, a digital world parallel to our physical world is slowly taking shape. By bringing together these fragments of data and integrating them into one digital space, we have given birth to the original Metaverse.
The outbreak of Covid-19 was another impetus for people to adopt the digital world. As we spend more time in the virtual world, big tech companies such as Microsoft, Google and Tencent saw opportunities and took the initiative. Facebook even renamed itself to Meta, pushing the Metaverse hype to a new climax.
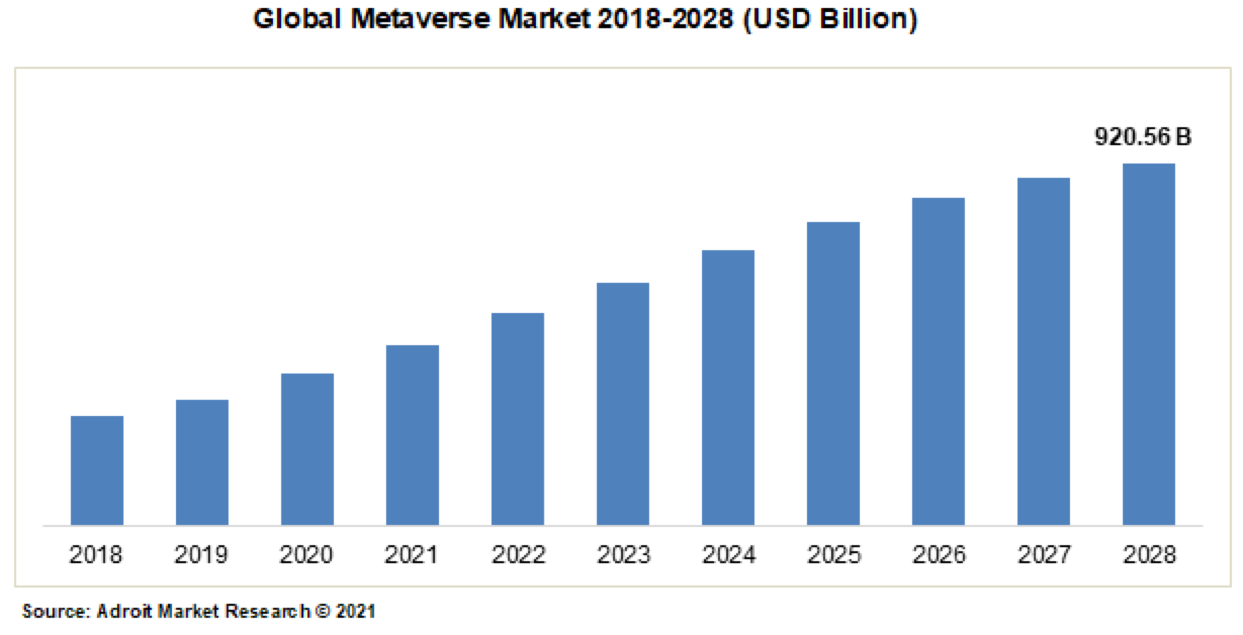
As unicorn companies and venture capitalists all put their eggs in the Metaverse, a brand-new era is peeping around the corner.
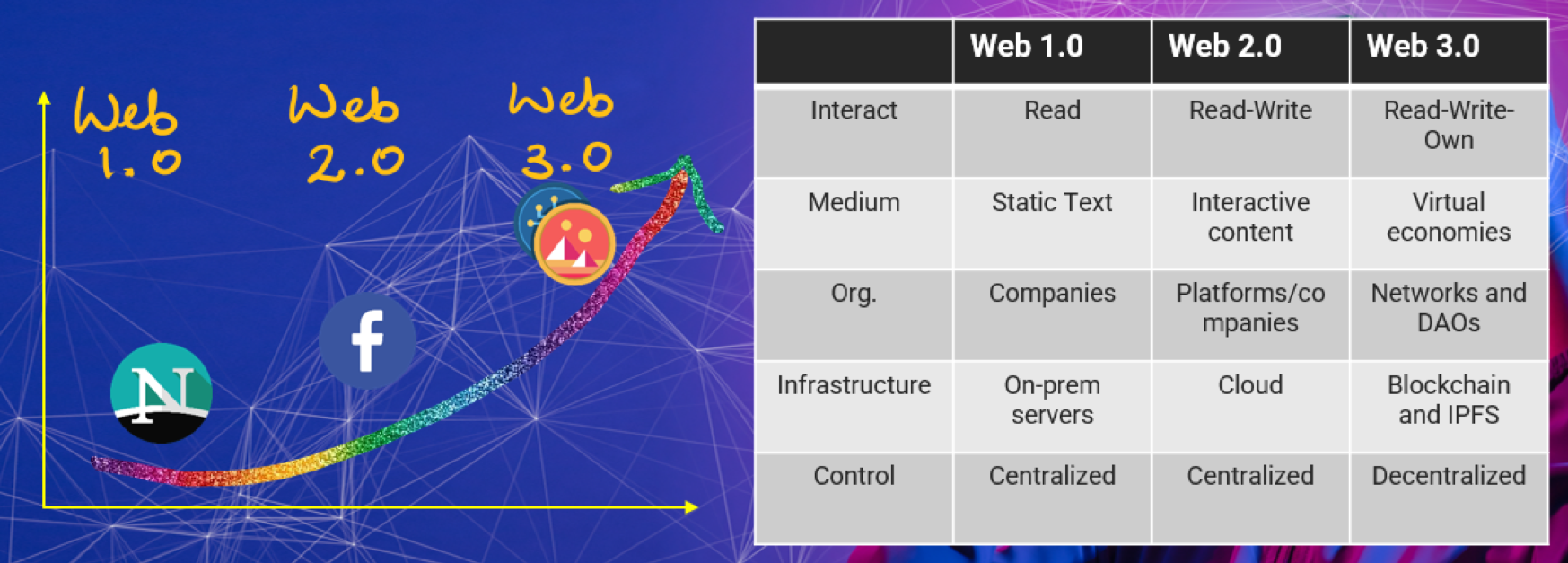
A Projection of the Development of the Metaverse
In the short term, the use scenarios of the Metaverse will focus on revolutionizing gaming, social media and other traditional entertainment industries. At this stage, immersive content consumption will be what sets the Metaverse apart. As MR technologies and devices become maturer, people’s experience in the Metaverse could see a quantum leap, and the Metaverse will become the primary medium of entertainment for most people. The explosion of Metaverse content due to its social networking nature will ignite the demand for 5G, boosting 5G coverage to an unprecedented level.
In the middle term, the Metaverse will gradually become part and parcel of people’s work and life. Today, digital twin is already a crucial technology in the manufacturing industry. As VR, AR and cloud computing gain wider adoption, the Metaverse will feature smart cities built on virtual networks, a closed-loop virtual economic system, digital services bridging the physical and the virtual worlds as well as maturer financial tools.
In the long term, the Metaverse will bring endless possibilities, revolutionizing the way society works by integrating the virtual and the physical worlds. People today are still debating what society will look like 30 years down the road when the Metaverse has reached its full potential, fundamentally altering the way we produce, organize and connect with each other. But needless to say, technological advances are always accompanied by new situations, problems and challenges.